How To Know The Difference
Androgenetic alopecia and hair loss caused by thyroid issues cause hair to fall out in distinct patterns. This allows doctors to easily distinguish between the two types of hair loss.
âHair loss from hypothyroidism is more diffuse and does not have a pattern,â physician and medical communications writer Leann Poston, MD tells WebMD Connect to Care. âIt involves the entire scalp. The ability to see the scalp through the overlying hair is typical.â
âMale pattern baldness or androgenic alopecia can occur in both men and women,â says Poston. âMen typically notice a thinning of hair on the top and front of the head above both temples. Women notice it more on the top and crown of the head. In women, the hairline does not recede as it does in men.â
If your doctor suspects that thyroid problems are causing your hair loss, they will run a blood test. âA diagnostic blood test can measure the Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone . Excess TSH usually indicates hypothyroidism, while abnormally low levels suggest hyperthyroidism,â hair loss specialist and hair restoration surgeon Abraham Armani, MD tells WebMD Connect to Care. âYour treating physician may prescribe a thyroid hormone medication to restore levels to normal.â
Read Also: What Type Of Zinc Is Best For Hair Loss
What Is The Thyroid
The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. Its main purpose in the body is to release hormones into the bloodstream, particularly triiodothyronine and thyroxine. Through the release of these hormones, the thyroid fulfils a number of very important body functions, including the regulation of the metabolism and the central nervous system.
If the thyroid gland ceases to operate as it should, it can have wide-ranging effects across the body, and one of these is hair loss. Because the body is not metabolising food into energy as it should, this can result in the hair follicles either shutting down or slowing the production of new hair. The nature of the hair loss experienced is usually diffuse thinning hairacross the whole scalp. The first signs of this might be finding more hair than usual on your hair brush or in the plughole.
The Life Cycle Of Hair
To identify the difference between normal hair loss and that related to a thyroid condition, itâs important to understand the three phases of the hair life cycle. These include:
Verywell / Emily Roberts
- Anagen phase: This is the growth phase, meaning your hair is actively growing. The rate of growth and duration depends on the type of hair and where itâs located. At any given time, about 90% of the hair on your scalp is in the anagen phase.
- Catagen phase: Hair then enters this âtransition phaseâ during which hair stops actively growing. This lasts about three weeks and involves less than 1% of the hairs on your scalp at a time.
- Telogen phase: During this last phase, a hair prepares to shed it is then pushed out of the follicle and falls out. Typically, about 50 and 150 telogen hairs are shed per day. These hairs are then replaced by new growth and the cycle begins again.
Thyroid-related hair loss and hair changes have some characteristic patterns, including:
- Diffuse hair loss/thinning across the whole scalp
- Hair loss that occurs in discrete areas of the scalp, resulting in smooth, circular bald patches
- Loss of body hair from areas other than your head: A unique and characteristic symptom of hypothyroidism is the loss of the hair on the outer edges of your eyebrows
- Changes in your hairâs texture: With hypothyroidism, your hair may become dry or coarse with hyperthyroidism, it can become extra soft and fine
You May Like: What Is The Best Vitamin Supplement For Hair Loss
Thyroid Disease And The Hair Loss Connection
Although hair loss is not a life-threatening condition, it certainly shouldnât be ignored. Like most diseases, there are several root causes of hair loss. For instance, hair loss has long been considered a common side effect of thyroid disease, which can be as harmless as an enlarged gland, or as life-threatening as thyroid cancer.
A 2011 retrospective study published in the journal Dermato-Endocrinology found an association between hair loss and thyroid abnormalities. Other studies suggest that thyroid disease can cause hair loss.
The thyroid is a small butterfly-shaped gland that produces hormones that influence every metabolic process in the body. Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are the most common types of thyroid disease. Hashimotoâs disease is the most frequent cause of hypothyroidism, and Graveâs disease is considered the top cause of hyperthyroidism. Since hair growth depends on the proper function of the thyroid gland, abnormal thyroid hormone levels will lead to hair loss if the thyroid disease is not treated.
Hypothyroidism will show lower levels of the thyroid hormones, triiodothyronine and thyroxine , in the blood. Too little thyroid hormones will produce hair loss on the head and other areas of the body. Hyperthyroidism will indicate higher levels of these thyroid hormones, and lead to thinning hair on the scalp.
Hypothyroidism And Hair Growth Retardation
Hypothyroidism can cause severe retardation of hair growth . The symptoms will be visible three months before the onset of the TE.
Its when the hair follicles slip into the state of rest. In most of the acute cases, the hair sheds without coming out of this phase.
Hyperthyroidism is one condition in which the thyroxin levels increase abnormally due to the hyperactivity of the thyroid gland. This phenomenon can lead to a condition of diffuse alopecia.
In many cases, it has been observed among children between the ages of 3 or 4. Its stated to be due to the decrease in the hair shaft tensile strength and the thinning of the shaft diameter.
Lets quickly observe the following conditions:
1. Proliferation Damages: Hyperthyroidism affects hair follicle and root sheath proliferation within the initial stages of ANAGEN.
It results in enhanced pressure on the follicles, bulb, and the rest of the shaft. The probability of breakdown increases significantly due to the proliferation of damages.
2. Metabolism Damages: The metabolism of the hair follicles and the shaft happens at the hair bulb due to the deposits of proteins and micronutrients.
Hyperthyroidism can lead to inefficient metabolism, leading to extensive hair loss. However, the exact links between hyperthyroidism and hair follicle metabolism damages have not been established so far.
3. Telogen Effluvium : As seen in the case of hypothyroidism, TE can occur in the hyperthyroidism condition as well.
You May Like: Can Shampoo Cause Hair Loss
Hair Transplant At Cosmedica
Medications are the primary solution for thyroid conditions, but getting a hair transplant in Turkey is a suitable treatment for thyroid hair loss.
Restoring your bodys thyroid function to normal takes a long time, and complete hair growth may take even longer. A quicker solution is to opt for a hair transplant.
At Cosmedica, you can undergo a hair transplant with medically reviewed techniques to have your hair follicles grow back in no time. This way, you can worry less about your hair loss problem and focus on treating your thyroid problems.
More to explore
You May Like: Can Alcohol Cause Hair Loss
Make Sure Youre On The Right Type And Dose Of Supplemental Thyroid Hormone
Once you know all of your thyroid levels, you can work with your doctor to make sure that youre on the right type and dose of supplemental thyroid hormone. Free T3, the active form of thyroid hormone, plays a big role in the health of your hair, yet the most commonly prescribed supplemental thyroid hormone is a T4-only hormone, such as Synthroid® or Levoxyl®. Many thyroid patients have difficulty converting T4, the storage form of the hormone, to Free T32, and do better on natural desiccated thyroid hormone, such as Armour® or Naturethroid®, which includes both T4 and T3, or by adding in a T3-only form of supplemental thyroid hormone, such as Cytomel® or a compounded time-release T3 formula. I discuss in detail all of the different forms of supplemental thyroid hormone in my book, The Thyroid Connection. Determining which supplemental hormone is right for you is a crucial step in reversing thyroid hair loss.
Recommended Reading: What Doctor Do You See For Thinning Hair
Hypothyroidism And Hair Loss
As weve said, thyroid levels and hair loss are inextricably linked. Hair loss due to thyroid is linked to hypothyroidism, low levels of thyroid hormones, which reduces the ability of the body to regenerate cells. Women are five times more likely to be diagnosed with hypothyroidism than men and the odds increase with age. According to the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the autoimmune disease Hashimotos thyroiditis is responsible for up to 80% of hypothyroid cases in the US and in the developed world. In the developing world, hypothyroidism often is caused by iodine deficiency. Endocrinologists advise that individuals with one autoimmune disease are more at risk for other autoimmune diseases. For instance, the hair loss condition alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the hair follicles. Thus, women who have hypothyroidism due to Hashimotos thyroiditis may be more susceptible to developing alopecia areata.
When To Contact Your Doctor
If youve checked off signs and are not feeling yourself, discuss this with your primary care doctor. These signs dont necessarily mean that you have thyroid disease. By asking you about your symptoms, your doctor can decide whether you need a blood test to check for thyroid disease.
Have a skin, hair, or nail problem?
Discover the benefits of seeing a dermatologist.
ImagesImage 1: Getty ImagesImages 2, 3, 4: Used with permission of the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 Jun 48:970-2.
ReferencesAi J, Leonhardt JM, et al. Autoimmune thyroid diseases: etiology, pathogenesis, and dermatologic manifestations. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 48:641-59.
Anderson CK, Miller OF. Triad of exophthalmos, pretibial myxedema, and acropachy in a patient with Graves’ disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003 48:970-2.
Bae JM, Lee JH, et al. Vitiligo and overt thyroid diseases: A nationwide population-based study in Korea. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 76:871-8.
Callen JP. Dermatologic manifestations in patients with systemic disease. In: Bolognia JL, et al. Dermatology. . Mosby Elsevier, Spain, 2008: 681-2.
Kalus AA, Chien AJ, et al. Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine diseases. In Wolff K et al. Fitzpatricks Dermatology in General Medicine . McGraw Hill, China, 2008:1470-4.
Recommended Reading: Can Colon Cancer Cause Hair Loss
How Can I Stop My Immediate Hair Fall
Vitamin D deficiency Vitamin D stimulates the hair follicles, resulting in hair growth. When a person does not get enough vitamin D, they may experience hair loss, alongside other symptoms. Some research has linked vitamin D deficiencies with alopecia areata. Learn about vitamin D deficiency and hair loss.
What Is The Link Between Parathyroid Disease And Hair Loss
Studies show hair loss in HPT patients is rare but, there is a significant prevalence of hair loss in patients dealing with hypothyroidism. In one study of 25 patients diagnosed with hypothyroidism, researchers found hair symptoms were present in 68% of patients. Researchers also noted that these symptoms impacted patients quality of life. Comparatively, a study of 21 patients diagnosed with hypoparathyroidism revealed 62% of patients reported axillary hair loss, 52% reported loss of pubic hair, and 48% reported coarsening of body hair.
Other research shows parathyroid hormone may impact hair follicle growth. PTH regulates calcium in the body, and an HPT patient may be dealing with an overactive parathyroid gland that produces too much PTH. However, the role of PTH and an abnormal parathyroid gland in hair growth remains unclear and continues to be studied.
Thinning hair is also a symptom of HPT. Conversely, outside of thinning hair, other HPT symptoms can occur.
Recommended Reading: How Can I Stop Hair Loss During Menopause
You May Like: How Do You Reverse Thinning Hair
Biology Of Thyroid Hair Loss
It all starts with the brain. Thyroid stimulating hormone is produced by pituiary glad located at the base of our brain. TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine , and then triiodothyronine . When it comes to hair growth, T4 stimulates hair matrix keratinocyte production and multiplication. Keratinocytes is a major cell type in the outer layer of the skin. In hair growth, keratinocytes play an especially important role, since they help forming hair follicles and help regulate stem cells of the follicle.
Both T3 and T4 also slow down apoptosis the death of keratinocyte cells. This further upholds and supports correct functioning of the hair follicle and healthy hair growth.
Also Check: Does Suave Cause Hair Loss
Make Sure Your Thyroid Labs Are Optimal

My first recommendation if you are dealing with thyroid hair loss is to have your doctor run a full thyroid panel to make sure your TSH, Free T4 , Free T3 , and Reverse T3 levels are all optimal1. In my article, What Your Thyroid Lab Results Really Mean, I explain what each of these blood tests measures, why your doctor needs to order all of them , and why they should use optimal rather than normal reference ranges. Its important to understand that you can still have thyroid dysfunction and symptoms, including thyroid hair loss, even if your TSH and T4 are normal, and the first step in optimizing all of your levels is to have them tested.
Recommended Reading: Does Collagen Help With Postpartum Hair Loss
Don’t Miss: Is Nioxin Shampoo Good For Hair Loss
Other Symptoms Of Thyroid Disease
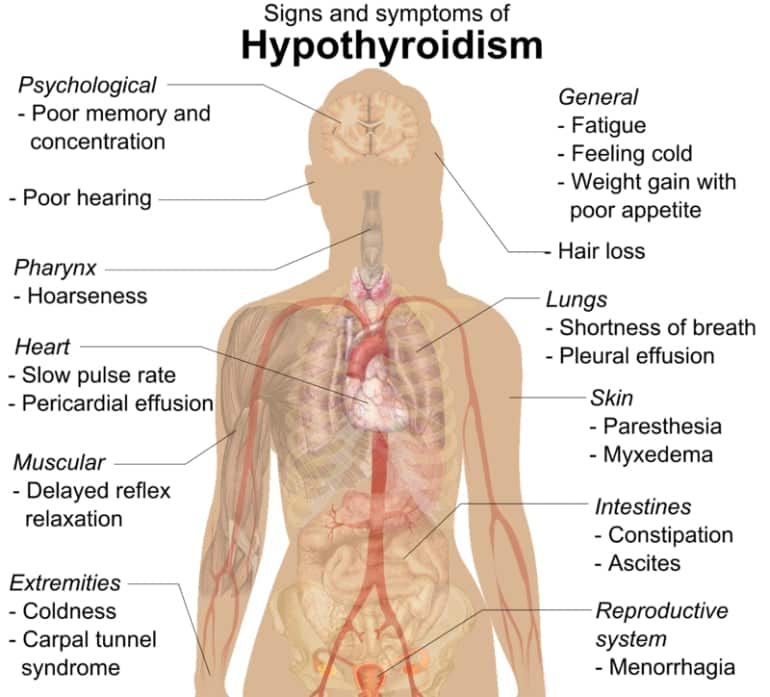
There are a variety of symptoms associated with thyroid disease. In addition to thinning hair, balding, and hair loss, other thyroid disease symptoms include:
- Mood changes such as depression, irritability, anxiety, and nervousness
- Thinning eyebrows, blurry vision, and dryness of hair or skin
- Carpal tunnel syndrome or tendinitis, and muscle pain or weakness
- Weight changes such as weight gain or weight loss, or water retention
- Insomnia, too much sleep, and lethargy
- Abnormal menstrual periods
- Cognitive impairment such as poor memory and concentration
- Problems tolerating cold and hot temperatures, tingling feet and hands
- Lowered immunity, recurring infections, and slow healing
- High cholesterol
What Is Thyroid Hair Loss
Thyroid related hair loss manifests when a person suffers long term hormonal imbalance resulting from abnormal behaviour of the thyroid. Hair loss appears far less common in short term thyroid related conditions. The thyroid produces hormones responsible for a range of important tasks including temperature, metabolic rate, maintenance of bone structures and heart rate. Both an overactive and underactive thyroid can cause hair loss. Hyperthyroidism, the overactive thyroid condition, occurs when the thyroid produces too many hormones. Hyperthyroidism is up to ten times more likely in men than women and is usually diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 40. Hair loss is a symptom of prolonged hyperthyroid issues.
Also Check: What Vitamins Do I Take For Hair Loss
How To Treat Thyroid
If your healthcare provider diagnoses you with a thyroid condition, youll likely be prescribed medication to treat your condition.
For hypothyroidism, your healthcare provider may prescribe a synthetic thyroid hormone such as Levo-T® or Synthroid®. These medications work by bringing your thyroid hormones up to a normal level.
For hyperthyroidism, your healthcare provider may prescribe an anti-thyroid medication such as Tapazole® or propylthiouracil. These medications stop your thyroid gland from producing overly high levels of thyroid hormones.
Depending on your symptoms, treatment for hyperthyroidism may include radioactive iodine and/or beta-blockers. Severe cases of hyperthyroidism are occasionally treated by removing some or all of the thyroid gland in a procedure known as thyroidectomy.
Most of the time, thyroid-related hair loss resolves on its own after you successfully treat the underlying condition. After treating your thyroid condition, it can take several months for your hair to start growing again.
You might be able to speed up this growth using minoxidil, a topical medication that improves blood flow to the scalp. Because thyroid-related hair loss isnt caused by DHT, finasteride isnt effective at treating or preventing this form of hair loss.
Recommended Reading: What Are Early Warning Signs Of Thyroid Cancer?
What Types Of Hair Loss Can A Thyroid Disorder Cause
The thyroid hormone is essential in the development of a healthy hair life cycle. It helps maintain the hair follicles from which your hair grows. And when the body has an excessive amount of the thyroid hormone or not enough of it, it can shock the body into a telogen phase. Telogen effluvium is a condition that occurs when the hair follicle enters the resting stage of the hair regrowth cycle too early. When this happens, you could experience more hair loss and alopecia patterns in a short space of time.
Alopecia areata differs from the shedding effect of telogen effluvium because it’s more patchy. It can be triggered by a thyroid disorder. This is because many people who have a thyroid disorder also have autoimmune thyroid disease. And when you have one autoimmune disease, you are more likely to develop another one, like alopecia areata.
Read: Here’s How Gut Health and Hair Loss Are Connected
Also Check: Is Aloe Vera Good For Your Hair Loss
Symptoms Of Thyroid Related Hair Loss
Slow and gradual thinning of hair is the most common symptom of thyroid related hair loss. You may notice more than usual hair lose while combing.
Furthermore, hair loss may develop slowly with hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. You wont necessarily see patches or bald spots on your scalp, but, your hair may seem thinner all over.
In most cases, hair loss caused by thyroid conditions is temporary, but regrowth of hairs may take several months.
It is important to note here that, you can still experience hair loss even after starting medicines for your thyroid condition. This is because the hair growth cycle is a months long process. But some people start wrongly blaming the thyroid medicines for hair loss. Unfortunately, if they stop their thyroid medicines, the hair loss problem will become worse.
Kindly note, it is perfectly normal to lose 50100 hairs from your head each day. However, hair loss beyond this needs medical attention and may be related to thyroid problem.