What Is The Relationship Between Hair Loss In Women And Menopause
During menopause, you might see one of two things happen with your hair. You might start growing hair where you didnt before. Or, you might see the hair you have start to thin. One cause may be changing levels of hormones during menopause. Estrogen and progesterone levels fall, meaning that the effects of the androgens, male hormones, are increased.
During and after menopause, hair might become finer because hair follicles shrink. Hair grows more slowly and falls out more easily in these cases.
Your healthcare provider will do a thorough examination and take a detailed history to help you deal with changes in hair growth. You may be directed to have your iron levels or thyroid hormone levels tested. Your medications might be changed if what you take is found to affect hair loss or growth.
The Hair Follicle Cycle
The hair follicle cycle is divided into three main distinct phases: the anagen, the catagen, and the telogen . Some authors also identify one additional phase: the exogen.
Hair growth phases: anagen , catagen , telogen , exogen .
The most prolonged phase is the anagen, which lasts 27 years. It is also called the growing phase. During this phase, cells divide rapidly at the lower part of the hair, while matrix cells migrate outward.
The catagen phase is a short transition period, which is defined as involution or regression. This phase lasts around three weeks. During this phase, the hair shaft loses the connections from the papillae and contracts.
The telogen phase can also be referred to as the resting stage. This phase can last about three months and is described as the regression of the matrix and retraction of the papilla to a location near the bulge. There is no significant proliferation or apoptosis during this phase.
The exogen phase is an additional distinct phase where the active hair shaft and new hair continue to grow.
At any given time, up to 8590% of the hair on the scalp remains in the anagen phase, whereas the remaining follicles are either in the catagen phase for 2% of the time or in the telogen phase for the remaining 1015% of the time . However, this percentage of telogen hair can be overestimated, with novel data indicating that only 3.6% remain in the telogen phase .
What Causes Menopausal Hair Loss
During menopause, levels of the hormones estrogen and progesterone go down. Because these hormones play a role in hair growth, hair loss can occur as they begin to drop. It can also lead to hair thinning and hair that doesnt grow as quickly as it normally would.
A decrease in progesterone and estrogen also sparks an increase in androgens, which are male hormones that are found in women in smaller amounts than in men. Androgens can cause the hair follicles on the head to shrink, resulting in hair loss.
Other causes can include high levels of stress as well as nutrient deficiencies.
Recommended Reading: How To Cover Up Hair Loss
Estrogen And Hair Loss: The Basics
-
Estrogen is one of the most important female sex hormones. Its responsible for several aspects of your health, including controlling your menstrual cycle and promoting optimal brain, bone, heart and skin health.
-
Before menopause, your body produces three forms of estrogen: estradiol, estriol and estrone. During menopause, your body stops producing estradiol and estriol, and only produces estrone.
-
Some women develop menopausal hair loss as they enter menopause in their 40s, 50s or 60s. Experts believe that reduced levels of estrogen and other hormones may play a role in menopausal hair loss.
-
Research shows that estrogen is linked to hair growth. For example, during pregnancy, when estrogen levels are high, its common for hair density to increase, with a reduced level of shedding. However, pregnancy hair loss could be common as well.
-
Hair loss medications like minoxidil for women and other hair care products can help to stimulate hair growth and keep your hair strong, full and healthy.
What Questions Might Your Healthcare Provider Ask To Diagnose And Categorize Your Hair Loss
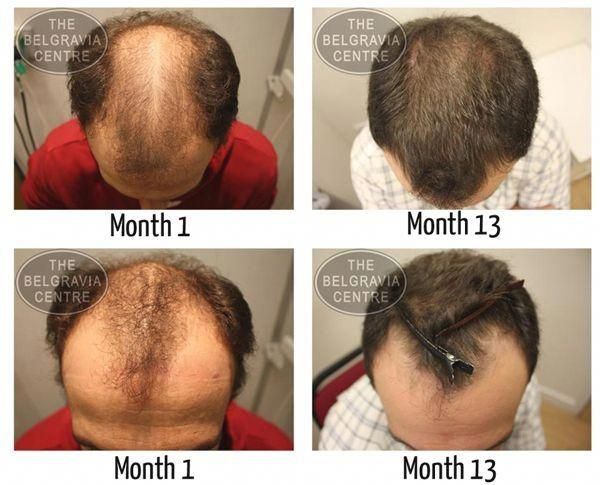
Your healthcare provider might ask about your habits:
- What kinds of hair products do you use?
- What kinds of hair styles do you wear?
- What types of food do you eat ?
- Do you have a habit of pulling your hair out ?
They might ask about your history:
- Has anyone in your immediate family experienced hair loss?
- Is there anything stressful going on in your life?
- What medications and supplements do you take every day?
- Has hair loss ever happened to you before?
- What foods are in your diet?
And, they might ask about your observations:
- How long have you been losing hair?
- Have you been shedding more?
- Have you noticed hair loss in places other than your scalp, like your eyebrows? Leg and arm hair?
- Does anything worsen your hair loss?
- Does anything improve your hair loss?
- Have you noticed hair loss occasionally or has it been going on continuously?
- Have you noticed if your hair growth has changed?
- Has your hair been breaking more often?
Recommended Reading: How Long To Take Finasteride For Hair Loss
Hair Loss In Menopause And The Role Of Estrogen
Hair problems increase before and after menopause. The main reason for hair loss in menopause is the reduction of the female hormone estrogen, which enriches and protects hair.
Although many women do not consider hair loss related to menopause, 40% of women experience hair loss in menopause. The increase in hair loss may start after age 45, which is defined as pre-menopause, or it can be seen 1-2 years after menopause. It can also occur at an early age in people who have entered menopause at an early age.
In the menopause period, the lack of production of estrogen and progesterone hormones, called female hormones, is not the same as it can affect whole-body metabolism, as well as hair growth. As a result of the decrease in estrogen, the male hormone Testosterone in the bloodstream does not increase, but it becomes the more dominant hormone and plays the leading role in the weakening of the hair.
The primary factor triggering hair loss in menopause is genetic predisposition. People with hair weakness in family history can see that this predisposition was triggered during menopause. Factors such as thyroid dysfunction, blood pressure problem, diabetes, insulin resistance, weight problem, intestinal problems and side effects of the drugs used can increase the degree of hair loss.
Symptoms of hair loss in menopause are as follows:
- The hair does not grow as before,
- Intense shedding,
- A decline in hair inlets.
Lifestyle And Habit Changes
If you have low estrogen levels due to a lifestyle factor for example, excessive exercise your healthcare provider may suggest making changes to increase your estrogen production.
You may need to adjust your activity level or diet. If youve experienced weight gain over time or are clinically obese, your healthcare provider may suggest losing weight. Other lifestyle changes, such as reducing your stress levels, may also help to promote optimal hormone production.
Read Also: Can Acupuncture Help Female Hair Loss
What Role Does Hormone Replacement Treatment Play In Hair Thinning During Menopause
Hormone replacement treatment during menopause may help with thinning hair if its related to hormone changes. Our provider may prescribe estrogen replacement therapy to help bring your hormones back into balance and back up to healthy baseline levels if you have low estrogen during menopause. This may help your hair in a few ways.
First, as we learned, estrogen plays a significant role during hair growth. Increasing estrogen levels during hormone replacement treatment may help your hair stay in the growing phase for longer than it would without hormone injections. It can also help your body keep testosterone levels in balance to help reduce the shrinking effects testosterone can have on hair follicles. In addition, some studies show that if you start hormone imbalance treatment early on for menopause symptoms, it may help you maintain your current hair density. This can help you reduce how much hair you lose throughout the course of menopause.
What Is The Connection Between Estrogen And Hair Loss
Estrogen and hair loss are connected through the natural hair growth cycle. Thinning hair is a common complaint of women during menopause and is a result of low estrogen levels. Likewise, pregnant women often have longer, fast-growing, thicker hair because of elevated estrogen levels. Hormones, medicines and disease can alter the length of the natural hair growth cycle.
Achieving hormonal balance is difficult for many reasons, especially for women between the ages of 35 and 50. Many women in their mid- to late 30s are overloaded with estrogen. By age 50, estrogen levels decrease by 35 percent, and progesterone levels decrease by 75%. Decreased estrogen and hair loss or thinning hair are common symptoms of menopause.
Estrogen replacement therapy is a common solution for decreased estrogen and hair loss in menopausal women, but the buildup of estrogen over time can lead to a medical condition known as estrogen dominance. This is an extreme imbalance of the two sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone. When estrogen levels are higher than progesterone levels, symptoms might include anxiety, breast tenderness and headaches, as well as irregular bleeding, water retention and weight gain. More serious risks are associated with taking a synthetic estrogen replacement, such as an increased risk for heart disease, breast cancer, blood clots, stroke and dementia.
You May Like: What Products Can I Use For Thinning Hair
Does Low Progesterone Cause Hair Loss
Hormones like testosterone and estrogen can play a key role in hair thinning and loss. However, progesterone is another such hormone, and low levelscan lead to hair loss in both men and women.
In this article, Im going to discuss the role that progesterone plays in hair loss. While it tends to play a bigger role in female hair loss, low levels of the hormone can affect males just the same.
Ill discuss the common causes of progesterone-related hair loss, as well as the treatment most recommended by doctors.
In addition, Ill touch upon FIVE ways you can naturally increase the levels of progesterone within your body. This will lessen the impact of progesterone-related hair loss, and may even enable you to regrow lost hair.
Clinical Evaluation Talk To Your Doctor
A laboratory workup for hair loss is commonly performed. Additional questions that you may be asked to help narrow down differential diagnosis are :
- When did the hair loss start? A sudden onset of hair loss may be suggestive of a disruption of the hair cycle.
- Where is the hair loss most prominent? Hair loss can be patchy, diffuse or patterned. Diffuse shedding may indicate disruption of the hair cycle, while patterned thinning could be attributed to hormonal dysregulation.
- What is the normal hair care routine? Certain hair care practices can have a tremendous impact on the loss of hair health.
With proper evaluation and appropriate testing for hormonal imbalances or nutritional deficiencies, help is on the way!
Also Check: What Can Prevent Hair Loss
Other Symptoms Of Low Estrogen
In addition to hair loss, low estrogen can cause a range of symptoms. Other symptoms of low estrogen include:
-
A reduced level of interest in sex
-
Less frequent menstrual periods, or no periods
-
Hot flashes and/or night sweats
-
Difficulty sleeping or staying asleep
-
Vaginal dryness and thinning of vaginal tissue
-
Dry skin
-
Mood swings
Some of these symptoms may occur before and during your period. For example, some women experience menstrual migraines painful headaches that occur before or during their period.
This is because your levels of estrogen fluctuate during your period. When estrogen levels are low, you may have a higher risk of experiencing the symptoms listed above.
How Can I Permanently Stop Facial Hair From Growing Naturally

5 home remedies to get rid of facial hair
Read Also: Can Parkinson’s Cause Hair Loss
What Did The Study Find
Of the participants, 52.2% experienced female pattern hair loss. Of those women, 73.2% had mild hair loss, 22.6% had moderate hair loss, and 4.3% had severe hair loss. Researchers found older age and higher body mass index were significantly associated with thinning hair. Additionally, the study found that 60% of participants experienced low self-esteem, and this increased with the severity of their hair loss.
Female pattern hair loss is the most common cause of hair loss in women. Its often identified as a widening part, receding temples, or thinning hair, according to the Jessica Shepherd, M.D., board-certified OB-GYN and chief medical officer of Verywell Health.
How Estrogen Affects Hair During Menopause
It is inevitable that the anxieties increase in women who have entered the menopause period. There are many questions about menopause, which has a very important place in womens life. Apart from hot flashes, weight gain decreased sexual desire and loss of thinning and elasticity of the skin, one of the things women are most concerned about is hair loss. In the female body that produces both estrogen and testosterone before menopause, hair loss is faced because the level of estrogen hormone together with menopause is less effective against testosterone hormone. With the continuation of the menopause process, hair loss can also increase.
The hair loss mechanism of women in this period is similar to that of men. Therefore, treatments for male pattern hair loss can be applied in its treatment. Menopause increases hair loss, but not every woman who enters the menopause will necessarily lose her hair. Because, in addition to hormones, genes also have an effect on hair loss during womens menopause. Approximately two-thirds of women who enter menopause have hair loss. Others only have thinning hair.
In the majority of polycystic ovarian patients, the male-type hair loss that develops as a result of the effect of increased androgen hormones and the hormone balance that deteriorates in women is a significant complaint, and with the treatment of the disease, hair loss stops and the hair grows again.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hair Back After Hair Loss