What Is Generalized Hair Loss
This is an overall hair thinning without specific bald spots or patterns. While this type of hair loss may not be noticeable to others, often the individual will feel their hair is not as thick or full as it previously was. Common conditions in this category are
Under normal conditions, scalp hairs live for about three years they then enter the telogen or resting phase. During the three-month telogen period, the hair root shrivels up into a small “club,” then the hair falls out. It is therefore normal to lose about 100 hairs every day, more of them on days when shampooing loosens the hairs that are ready to fall out. The body then replaces the hairs.
Sometimes people who worry about losing their hair start noticing hairs on their pillow or in the sink, not realizing that they’ve always been there. A close look at these will usually reveal the club at the end, showing that these hairs are shed normally.
- Normally, about 10% of scalp hairs are in the telogen phase.
Several circumstances produce a “shock to the system” that alters the hair growth rhythm. As a result, as much as 30%-40% of the hairs can cycle into telogen. Three months later, hairs come out in a massive shedding , especially near the front of the scalp. These include
- severe illness,
- severe emotional stress or loss.
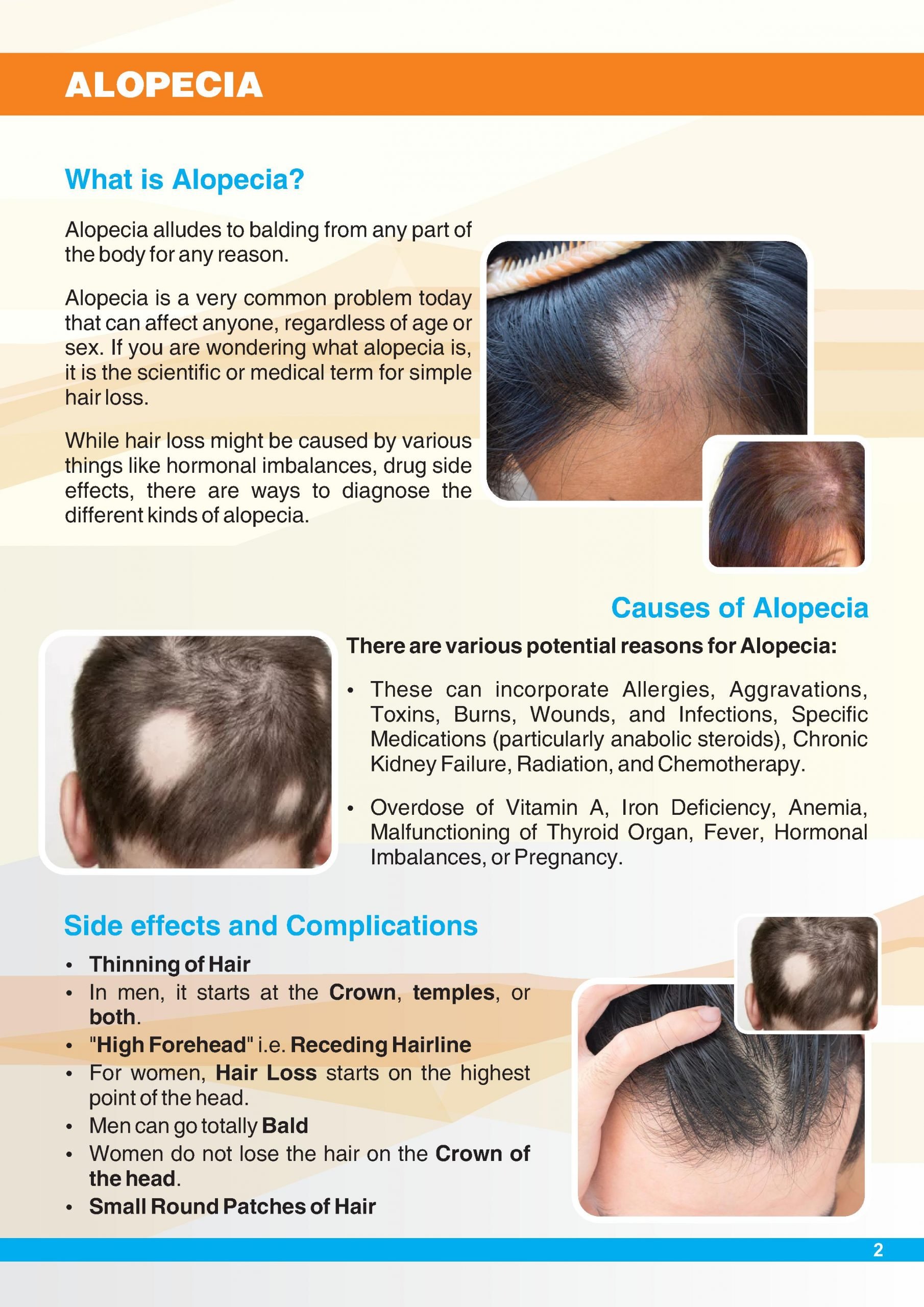
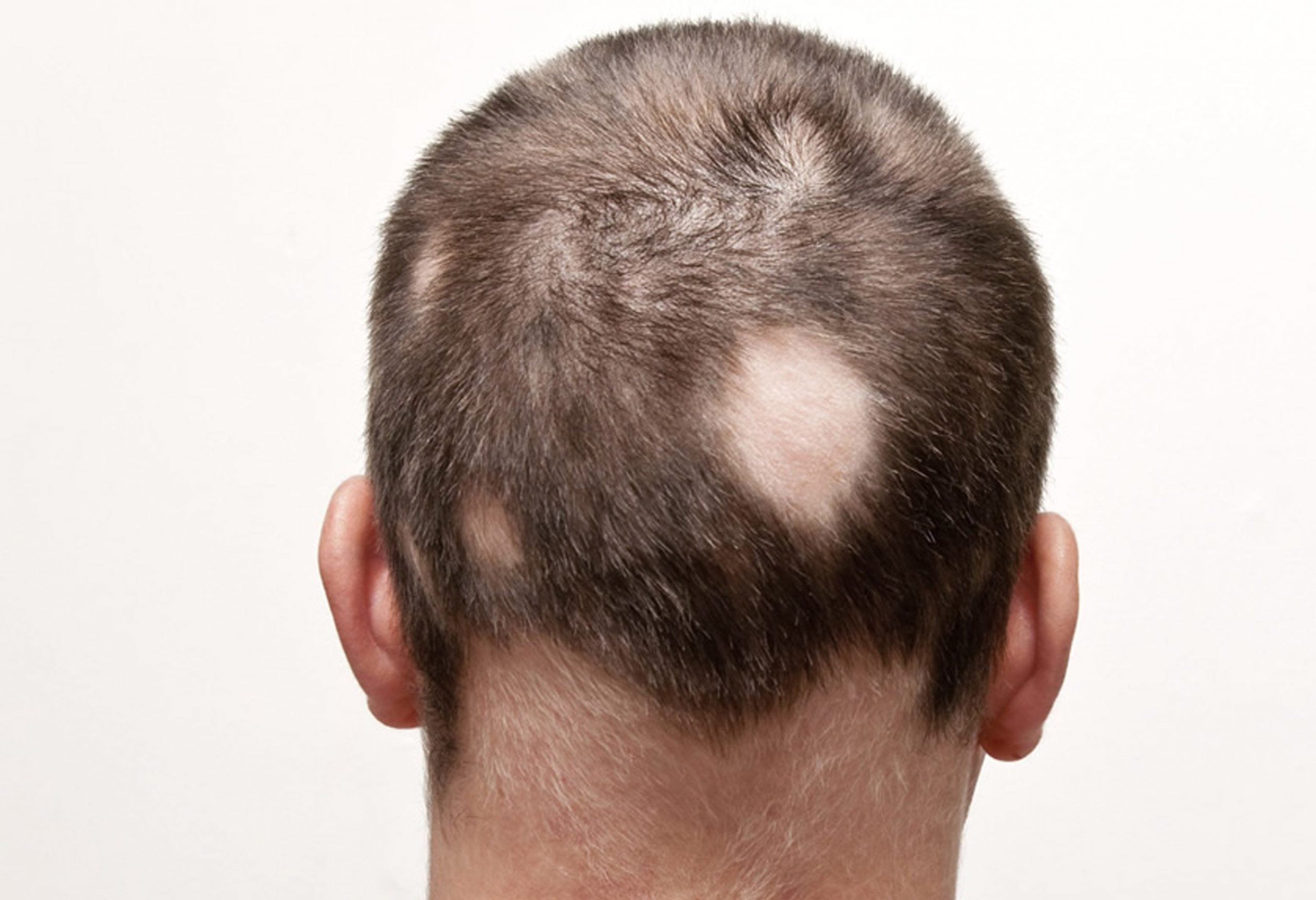
What Is Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is a disease that causes hair loss. In alopecia areata, the immune system attacks the structures in skin that form hair .
Alopecia areata usually affects the head and face, though hair can be lost from any part of the body. Hair typically falls out in small, round patches about the size of a quarter. In some cases, hair loss is more extensive.
Anyone can have alopecia areata:
- Both men and women can get it.
- It affects all racial and ethnic groups.
- It can happen at any age, but most people get it in their teens, 20s, or 30s.
If you have a close family member with the disease, you may have a higher risk of getting it, but for many people, there is no family history.
People with certain diseases, such as psoriasis, and those with allergic conditions such as hay fever are more likely to get alopecia areata.
Female Pattern Hair Loss
In women, hair slowly thins all over the scalp, but the hairline usually doesnt recede. Many women experience this type of hair loss as a natural part of aging, although hair loss may begin any time after puberty. Female pattern hair loss can cause hair to thin dramatically, but only rarely does it lead to baldness.
Read Also: What Supplement For Hair Loss
Are There Complications/side Effects Of Treatment
Minoxidil may irritate your scalp and cause dryness, scaling, itching and/or redness. See your dermatologist if this happens.
With Minoxidil you might also see hair growing in other places other than your scalp . Wash your face after you apply Minoxidil and make sure you avoid other areas when you apply it.
Bacterial And Fungal Skin Infections
Cats can get skin infections from either bacterial or fungal microorganisms. Skin infections in cats occur as either uncomplicated infections or secondary to a possible inflammatory or allergic skin problem. Infection-induced alopecia occurs when a bacterial or fungal microorganism penetrates the skins protective barriers and grows within the superficial layer of the skin. This destroys hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
Severe bacterial skin infections often result in moist dermatitis with skin inflammation. Fungal infections tend to cause severe dryness coupled with inflamed skin. Uncomplicated infections are easily treated with systemic or topical antibacterials and antifungals. For secondary infections, the underlying condition needs to be addressed as well for the treatment to work.
Recommended Reading: What Is Hair Loss Caused By
Treatment For Hair Loss
Most hair loss does not need treatment and is either:
- temporary and it’ll grow back
- a normal part of getting older
Hair loss caused by a medical condition usually stops or grows back once you’ve recovered.
There are things you can try if your hair loss is causing you distress. But most treatments are not available on the NHS, so you’ll have to pay for them.
No treatment is 100% effective.
What To Do If You Think You Have Alopecia Barbae
If youre seeing patchy hair loss, interrupted beard growth and other signs of alopecia barbae, your first priority should be consulting a healthcare professional particularly if you have no known autoimmune disorders.
Facial hair loss due to treatable medical conditions is something that needs immediate attention, and autoimmune diseases need to be managed as soon as possible.
A healthcare provider may recommend different treatments, whether for the disease itself or for hair loss or both.
Its possible youll still see permanent hair loss even with help, and chronic hair loss issues may recur unpredictably.
But having a professional helping to monitor your condition is the best tool to help you combat the beard problems.
Also Check: How To Style Mens Thin Hair
What Is Alopecia Barbae
To understand alopecia barbae, you need to understand its parent hair loss type: alopecia areata.
Alopecia areata is a type of hair loss caused by autoimmune diseases, which can cause the body to damage hair follicles.
With alopecia areata, your autoimmune system mistakenly sees your hair follicle as an invader and attacks your follicles as if they are foreign bodies.
The damage done by this can cause temporary hair loss, which will eventually become permanent if the damage is not addressed.
Alopecia areata is not contagious, and often develops during a persons teenage years. It can happen once, or in unpredictable and recurring cycles.
The American Academy of Dermatology Association says that alopecia areata can manifest in a variety of ways, with the hair loss being patchy in one location or widespread.
Worse, those patches of hair loss can even jump from one part of the body to another, healing and reappearing in new places.
Typically, alopecia areata affects the scalp, but it can frequently affect other body hair as well .
What Causes Hair Loss
First, your doctor or dermatologist will try to determine the underlying cause of your hair loss. The most common cause of hair loss is hereditary male- or female-pattern baldness.
If you have a family history of baldness, you may have this type of hair loss. Certain sex hormones can trigger hereditary hair loss. It may begin as early as puberty.
In some cases, hair loss may occur with a simple halt in the cycle of hair growth. Major illnesses, surgeries, or traumatic events can trigger hair loss. However, your hair will usually start growing back without treatment.
Hormonal changes can cause temporary hair loss. Examples include:
- heart problems
A physical or emotional shock may trigger noticeable hair loss. Examples of this type of shock include:
- a death in the family
- extreme weight loss
- a high fever
People with trichotillomania have a need to pull out their hair, usually from their head, eyebrows, or eyelashes.
Traction hair loss can be due to hairstyles that put pressure on the follicles by pulling the hair back very tightly.
A diet lacking in protein, iron, and other nutrients can also lead to thinning hair.
You May Like: What Is Good To Stop Hair Loss
Causes Of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition. An autoimmune condition develops when the immune system mistakes healthy cells for foreign substances. Normally, the immune system defends your body against foreign invaders, such as viruses and bacteria.
If you have alopecia areata, however, your immune system mistakenly attacks your hair follicles. Hair follicles are the structures from which hairs grow. The follicles become smaller and stop producing hair, leading to hair loss.
Researchers dont know the exact cause of this condition.
However, it most often occurs in people who have a family history of other autoimmune conditions, such as type 1 diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis. This is why some scientists suspect that genetics may contribute to the development of alopecia areata.
They also believe that certain factors in the environment are needed to trigger alopecia areata in people who are genetically predisposed to it.
How Long Does Hair Loss Last
In half of patients with alopecia areata, individual episodes of hair loss last less than one year, and hair grows back without treatment. These patients may experience recurrent episodes of hair loss that spontaneously regrow or respond quickly to treatments.
Other patients have a progressive course with more stubborn hair loss that does not grow back on its own and may not respond to different treatments.
At this time, there are no means to predict which patients will have limited and brief involvement and which patients will have extensive hair loss of a longer duration.
Don’t Miss: Which Shampoo Is Best For Thin Hair
What Causes Alopecia Barbae
Alopecia barbae is a particular type of localized hair loss due to alopecia areata affecting just your beard. It is caused by an autoimmune process in the body.
It has been found that people with certain autoimmune disease types, from hay fever to vitiligo, thyroid diseases to atopic dermatitis, asthma and even Down syndrome are at a higher risk of developing alopecia areata and, by extension, alopecia barbae.
Alopecia barbae is sometimes hard to understand, as it can cause patchy beard hair while your full head of hair is intact just inches away.
Autoimmune hair loss can be associated with other diseases, as well.
Some of them include lichen sclerosus et atrophicus, pemphigus foliaceus, morphea, hypothyroidism, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis , Addison’s disease, pernicious anemia, lupus erythematosus, lichen planus, endemic goiter, and diabetes mellitus.
Its not entirely clear who is and isnt likely to deal with patchy beard hair loss. One study suggests that youre more likely to suffer from alopecia areata if youre hispanic or black.
However, the study only included women, and researchers noted a need for more studies to be conducted.
What Are Some Tips For Dealing With Hair Loss In Women
There are some things you can do on your own. You might check with your stylist or try some of these:
- Coloring your hair adds volume to the strands, making your hair seem fuller.
- Massaging your head, like when you are washing your hair, can stimulate blood flow to the scalp and hair follicles.
- Getting your hair cut shorter, and having layers added, can make your hair seem fuller.
- Using the right kind of shampoo can also help. Look for a shampoo that adds volume without using sulfate detergents.
- Using the right kind of product at the right time can also help. There are products that add volume that you add while your hair is still wet. However, using too much product can add weight.
Recommended Reading: Does Ulcerative Colitis Cause Hair Loss
Infections That Cause Hair Loss
A number of infections and illnesses can lead to hair loss. An infection that causes a high fever, a fungal skin infection, and bacterial infections like syphilis can all be responsible for balding or thinning hair. Treating the underlying infection can restore hair growth and prevent future hair loss. So your first step is to seek medical attention for the primary health problem.
Can A Vitamin D Deficiency Cause Alopecia Areata
Studies have found that people with certain autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis or rheumatoid arthritis, have a vitamin D deficiency.
Because alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease, scientists have looked at the vitamin D levels in people who have alopecia areata. Some people did have a vitamin D deficiency, but others didnt. More research is needed before we know whether low levels of vitamin D play a role in causing this disease.
Also Check: Where To Buy Thinning Shears For Hair
What Is Tinea Capitis
Tinea is the medical word for fungal infection, and capitis means head. Tinea capitis is a fungal infection of the scalp that for the most part affects school-age children.
- Tinea capitis is more common in black African or African-American scalps.
- This condition is rare in healthy adults.
- Bald spots usually show broken-off hairs accompanied by dermatitis.
- Oral antifungals can penetrate the hair roots and cure the infection, after which hair grows back.
- Sharing hats or combs and brushes may transmit tinea capitis.
Hair Loss From Thyroid Problems
Either an underactive thyroid, a medical condition called hypothyroidism, or an overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism, can result in hair loss because each condition causes a hormonal imbalance. Hormones help to regulate nearly every function in the body, including hair growth. Getting the right treatment to control either of these thyroid conditions will get hormones under control, stop hair loss, and allow your hair to starting grow back.
Recommended Reading: Why Is My Hair Thinning At 18
Signs Of Alopecia Areata
While a loss of hair on the head is the most obvious sign of alopecia areata, the condition can also cause changes to your nails or hair loss on other places of your body. Below are some common signs of alopecia areata:
- Round or oval patches of hair loss on your scalp
- Round or oval patches of beard hair loss
- Band-shaped hair loss on the sides and lower back of your scalp
- Loss of eyelashes
There are several types of alopecia areata, including:
Alopecia areata
This is the most common form of alopecia areata and includes one or more coin-sized round or oval patches of hair loss. The hair loss can occur on your scalp or any area of your body where hair grows. This type of alopecia areata may progress into other types of alopecia, or it may stay patchy.
Persistent patchy alopecia areata
In persistent patchy alopecia areata, hair loss continues to be patchy for a long time without ever becoming more extensive.
Alopecia totalis
With alopecia totalis, hair loss occurs over your entire scalp.
Alopecia universalis
Alopecia universalis results in total hair loss on all parts of your body, including your scalp, face, and pubic area.
Diffuse alopecia areata
Diffuse alopecia areata can be confused with other types of hair loss, such as telogen effluvium or male- or female-pattern baldness. It is characterized by a sudden thinning of hair on the scalp.
Ophiasis alopecia
Eat A Healthy And Well
It probably comes as no surprise that a healthy diet filled with fresh foods, healthy proteins and fats is important for growth. Since inflammation is part of many autoimmune disorders, consider giving extra love to foods with anti-inflammatory benefits like tomatoes, green leafy vegetables, avocados and berries.
To help you get all the vitamins, minerals and nutrients you need, VEGAMOUR has carefully crafted supplements to support your hair wellness routine. Our all-vegan GRO Biotin Gummies contain a proprietary blend of vitamins and minerals to support the growth of beautiful strands by supporting your follicles from the inside out.
Or, support your gut and scalp microbiomes with our GRO WELL Hair Boost Supplement Powder + Probiotic, a delicious variety of adaptogen/probiotic drink mixes made from vital, vegan nutrients that are clinically proven to help promote visibly thicker, fuller, longer-looking hair.
Recommended Reading: Can I Use Minoxidil For Frontal Hair Loss