What Causes Hair Loss In Women
When most people hear the words hair loss, they think of balding men. However, hair loss can also be a significant problem for women. Female hair loss can occur for several reasons, from a genetic sensitivity to certain androgenic hormones to reactive factors.
Weve listed the most common causes of female hair loss below, as well as the specific ways in which each cause can affect your hairline.
What Causes Menopausal Hair Loss
A recent study shatters the misperception that losing hair in midlife is something only men need to worry about. This study found that more than 50% of women after 50 have visible female pattern hair loss that negatively impacts their self-image well being. It is believed that the hormonal fluctuation that happens during perimenopause and menopause is why women experience hair loss. During perimenopause and menopause, the change in hormone levels specifically the decreased production of estrogen and progesterone leads to thinning hair. That is because these hormones help keep hair in the growing phase , meaning these hairs stay on the head for longer.
The effects of androgens also increase during this time. These hormones shrink hair follicles, leading to thinner hair, and are responsible for unwanted hair growth in other body areas , which many women experience during menopause. With this type of female pattern hair loss, it is unlikely to experience bald spots or complete baldness. Instead, they’ll usually see general thinning throughout the hair.
Low Estrogen And Hair Loss
While pregnancy encourages hair growth due to higher estrogen levels, lower estrogen levels can have the opposite effect.
Low estrogen levels are most common during menopause, but it can happen to women at any age. As estrogen levels decline, the greater influence of testosterone shortens the growth phase, and the subsequent hair loss is usually gradual but can become noticeable over time. Hair loss caused by changing estrogen levels tends to be visible all over the scalp or evident in a widening part, rather than missing patches of hair or a horseshoe pattern as with male pattern baldness.
Its common for women to experience shedding hair after pregnancy. Usually, this is in response to estrogen levels returning to normal, shedding the extra hair grown during pregnancy. Usually, the hair will return to the same thickness it was before you got pregnant. New moms who are not breastfeeding should consider taking hair growth vitamins post-pregnancy too to balance out their hair growth cycle.
Don’t Miss: Does Psoriatic Arthritis Cause Hair Loss
Caring For Your Hair And Skin In Menopause
My hair, nails and skin look amazing since menopause started, said no perimenopausal or postmenopausal woman EVER! BUT that does not mean all hope is lost. On the contrary, there is a lot of easy and effective actions to take.
In general, skin and hair appearance are a reflection of what our body is trying to tell us. We are what we eatso lets start with the nitty gritty about diet and nutrients:
TAKE HOME POINT: for most women- a daily multivitamin is really all you need.
Try A Few Key Supplements

If youre wondering what vitamins are good for hair loss during menopause, there are a few key nutrients you need. Biotin and Viviscal, for example, come up again and again in perimenopausal hair loss research. Deficiencies in biotin are rare, but many women take supplements because it seems to improve the condition of their hair and nails.
Viviscal has Biotin in it and calcium. And vitamin C. It also contains shark cartilage, oyster extract, and a marine complex which is apparently the secret elixir that gives the ingredient its power. The U.S. National Library of Medicine published an article with a double-blind placebo controlled study that showed the efficacy of this product significantly more women who took Viviscal than the placebo noticed hair growth after 90 days, and even more after 180 days.
Now its true that the funding for the study was provided by the makers of Viviscal, but double-blind is double-blind. Furthermore, in an entirely separate article, Beauty Editor writer Katrina Persad tried Viviscal for six months and documented her results in a quite convincing photo essay and article that showed fairly dramatic results and Viviscal did not pay her for her trouble.
Check out this list of nutrients for hair loss, and where you can find them.
Also Check: How To Stop Thinning Hair On Top Of Head
The Hair Follicle Cycle
The hair follicle cycle is divided into three main distinct phases: the anagen, the catagen, and the telogen . Some authors also identify one additional phase: the exogen.
Hair growth phases: anagen , catagen , telogen , exogen .
The most prolonged phase is the anagen, which lasts 27 years. It is also called the growing phase. During this phase, cells divide rapidly at the lower part of the hair, while matrix cells migrate outward.
The catagen phase is a short transition period, which is defined as involution or regression. This phase lasts around three weeks. During this phase, the hair shaft loses the connections from the papillae and contracts.
The telogen phase can also be referred to as the resting stage. This phase can last about three months and is described as the regression of the matrix and retraction of the papilla to a location near the bulge. There is no significant proliferation or apoptosis during this phase.
The exogen phase is an additional distinct phase where the active hair shaft and new hair continue to grow.
At any given time, up to 8590% of the hair on the scalp remains in the anagen phase, whereas the remaining follicles are either in the catagen phase for 2% of the time or in the telogen phase for the remaining 1015% of the time . However, this percentage of telogen hair can be overestimated, with novel data indicating that only 3.6% remain in the telogen phase .
Causes Of Hair Loss In Women
Androgenetic alopecia, a type of hair loss commonly called male or female pattern baldness, was only partially understood until the last few decades. For many years, scientists thought that androgenetic alopecia was caused by the predominance of the male sex hormone, testosterone, which women also have in trace amounts under normal conditions. But while testosterone is at the core of the balding process, dihydrotestosterone is now thought to be the main culprit.
DHT, a derivative of the male hormone testosterone, is the enemy of hair follicles on your head. Simply put, under certain conditions DHT wants those follicles dead. This simple action is at the root of many kinds of hair loss.
Testosterone converts to DHT with the aid of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase. Scientists now believe that it’s not the amount of circulating testosterone that’s the problem but the level of DHT binding to receptors in scalp follicles. DHT shrinks hair follicles, making it impossible for healthy hair to survive.
The hormonal process of testosterone converting to DHT, which then harms hair follicles, happens in both men and women. Under normal conditions, women have a minute fraction of the level of testosterone that men have, but even a lower level can cause DHT- triggered hair loss in women.
Hair loss can also be caused by an imbalance of thyroid hormones or pregnancy, disease, and certain medications, which can all influence hair’s growth and shedding phases.
Show Sources
Read Also: What To Take For Hair Loss After Gastric Sleeve
Does Estrogen Cause Hair Loss In Men
Trying to figure out what causes hair loss in men has been a topic of scientific study for years. Thankfully as technology, and our understanding of science, evolves, we are able to test more theories and get a better idea of what factors may lead to male pattern baldness and general hair loss.
Weve talked before about hormones, specifically testosterone, and its effect on hair loss, but what about estrogen? Can having higher levels of estrogen in your body, as a man, cause you to lose your hair prematurely?
While male pattern baldness is usually related to genetics and age, there are some external factors that can speed up the hair loss process, or even cause you to begin losing your hair. Sometimes this hair loss is temporary, but there are times where it can be permanent as well.
If youre concerned about your hair thinning or falling out, its important to have a general understanding of how the elements in your body can have a positive or negative effect on your hair, especially the hormones in your body.
How To Hide Thinning Hair After Menopause
If hair continues to thin after menopause and natural treatments have been ineffective, there are things that can help camouflage this issue. Some hair stylists will suggest shortening the length of hair. This adds volume and reduces the weight of hair. It can also help hide problem spots.
Some more permanent but also costly options include topical hair growth products, hair extensions, wigs, surgical hair transplants, and low-level laser scalp treatments.
Recommended Reading: What’s The Best Extensions For Thin Hair
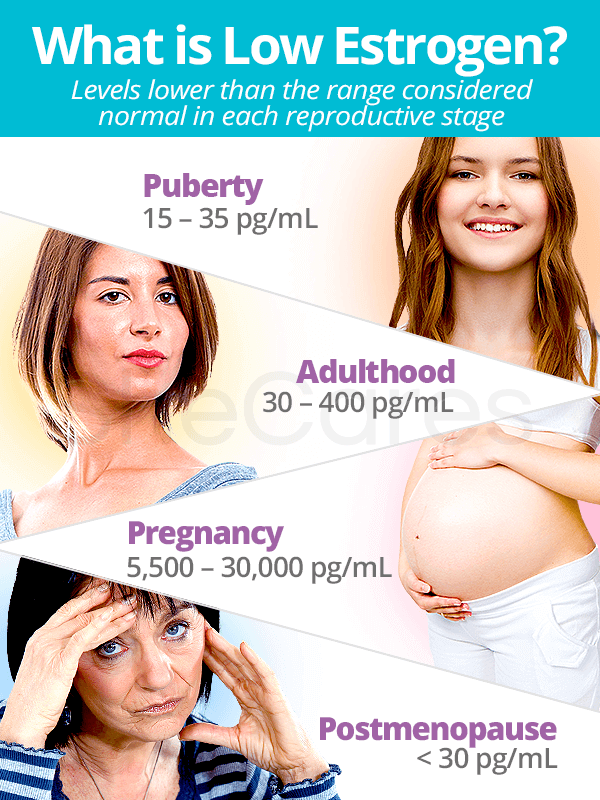
Who Does Low Estrogen Impact Most
Estrogen affects people assigned female at birth most. But everyones bodies make estrogen.
Youre most likely to be impacted by low estrogen if:
- Youre experiencing menopause or postmenopause. Your ovaries make the majority of your estrogen in your reproductive years. During menopause and postmenopause, your menstrual cycle stops and your ovaries no longer make estrogen. Instead, fat cells start making the majority of your bodys estrogen. Menopause officially begins when you havent had a period for twelve consecutive months. Postmenopause is the period that follows.
- Your ovaries were removed or injured during treatment. Your body will only produce small amounts of estrogen if your ovaries were removed as part of treatment for a condition . Similarly, radiation therapy can injure your ovaries so that they produce small amounts of estrogen.
What Medications Treat Low Estrogen
Hormone replacement therapy is a common treatment for low estrogen, especially during menopause and postmenopause. With HT, you take synthetic forms of estrogen and/or the hormone progesterone to boost your levels. There are two types of HT, estrogen therapy and estrogen progesterone/progestin hormone therapy . Providers prescribe the lowest doses possible to treat your symptoms while preventing side effects.
The only FDA-approved reasons for body-wide hormone replacement therapy are low bone mineral density and hot flash treatment, typically in the form of pills or patches. Vaginal estrogen in the form of rings, creams, and vaginal inserts are formulated to treat vaginal dryness and painful intercourse. Sometimes “body wide” estrogen can affect the vaginal tissue. Sometimes it doesnt. Vice versa, vaginal estrogen is not approved for the treatment of hot flashes.
Its not unusual to need vaginal estrogen in addition to body-wide estrogen if youre experiencing hot flashes and painful sex.
Estrogen therapy
Youll take estrogen supplements only, with no progesterone. Your provider will only prescribe this therapy if you no longer have a uterus .
Estrogen progesterone/progestin hormone therapy
HRT isnt without risks. Research has shown that long-term use of combination therapy may increase your risk of breast cancer, blood clots, heart attacks and stroke.
Recommended Reading: What Is Male Pattern Hair Loss
Female Pattern Hair Loss In General
Hair loss in women is usually caused by hormonal causes or mineral deficiency in the body. This situation may not be prevented with methods such as zinc, vitamin B supplements, and mesotherapy. Hair loss may occur if there is a problem in the absorption of these minerals due to zinc or selenium deficiency and chronic intestinal disease. Rheumatic diseases can also cause this problem. In these cases, the problem of baldness or hair loss improves when the missing mineral is replaced or the disease is treated.
Androgenetic hair loss, which is caused by a lack of minerals in the body, is observed in 90 percent of men and 45-50 percent of women. Androgen hormone in men and women plays a variable role in the emergence of this condition, such as genetic predisposition and aging and stress that will trigger these two causes. If the person is genetically predisposed and has the androgen hormone in his body, his hair will be lost at some point in his life. Hair loss can occur in approximately 30 percent of men aged 30 and 40 percent of those aged 40.
What Treatments Are Available For Hair Loss During Menopause
It’s important to note that, while hair loss around mid-life is generally menopause-related, there are a wide variety of additional factors that can lead to hair loss stress, poor diet, thyroid disorders, and certain medications can all be triggered. Here are the treatments that can minimize and prevent further hair loss during menopause.
Minoxidil
Minoxidil is a frequently used medication that the FDA has approved to treat male and female pattern hair loss. Minoxidil is applied topically to the scalp, increasing blood flow to this area, preventing further hair loss, and supporting hair regrowth. Generally, with consistent use, you’ll begin to see hair loss slow down after about two months and new growth around the four-month mark. There are some side effects to be aware of, including dryness, irritation, and itching of the scalp.
One thing to keep in mind is that consistency and long-term commitment are key with minoxidil. You need to continue its use to maintain hair growth, so this is not a short-term treatment option. While you can get minoxidil products over-the-counter, it’s a good idea to talk to a medical professional about whether it’s a suitable option for you and decide which strength is best for your needs.
Collagen peptides
How do collagen supplements improve hair quality?
Phytoestrogens: Benefits for women with menopause-related hair loss
Other things to do to support healthy hair during menopause
You May Like: What Kind Of Dr Do You See For Hair Loss
Estrogen And Oral Contraceptive Drugs
The role of estrogen and progestogen drugs in the treatment of hair loss and growth is also unclear. Estrogen is made when androstenedione or testosterone are modified by the enzyme aromatase. It is synthesized in the ovary and other peripheral tissues and then travels to its receptors, some of which are located in scalp hair follicles . At the scalp follicle, estradiol has been reported to induce aromatase activity . Estrogen has been hypothesized to have a protective role against hair loss on the basis of the observation that patients with lower estrogen levels during menopause, postpartum, or treatment with aromatase inhibitors or selective estrogen receptor modulators are more likely to develop FPHL . Another supporting observation is that in the frontal hairline of women, which tends to be spared with FPHL, there is a higher level of aromatase enzyme when compared with the rest of the scalp . This variation in hair loss could be the result of locally increased levels of estradiol or decreased levels of testosterone and DHT that is secondary to greater amounts of conversion.
How Common Is It
Female hair loss is a common condition, especially in the years surrounding menopause. According to the Cleveland Clinic, it is estimated that over 50% of women experience hair loss. Age, diet, ethnicity, and genetic factors all influence your chances of experiencing hair loss throughout your life, including during and after menopause.
Also Check: How Can I Make Thin Hair Thicker
Is Estrogen Good Or Bad For Your Hair
There is some confusion about estrogens direct effect on the hair follicle. On the one hand, the enzyme P450 aromatase is located in the follicles on the scalp. Women have far more aromatase than men do, especially in the front hair line and back of the scalp. Medical opinion states that the presence of estrogen is why women with alopecia usually retain their frontal hair line and the hair in the back of the scalp.
But estrogens seem to also have anti-hair properties. The discovery that 17–estradiol indeed exert hair growth inhibitory properties in female organ-cultured occipital scalp hair follicles role that for other authors may even exceed that of androgens. It seems like estrogens balance out androgenic effects in certain parts of the scalp, but cause hair loss in other parts of it. New discoveries are always proving known facts wrong, arent they? If estrogens might be a direct cause of hair loss in women, that forces us to adjust our beliefs about it.
The Typical Hair Loss Experience
On average, a person loses around 100-200 hairs a day to allow for new hair growth. During menopause, when your hair is breaking, it may seem that you are losing more than the average amount. In reality, however, your hair is not falling out but breaking somewhere along the hair strand itself, giving the appearance of thinner hair.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Hair Loss Treatment For Women